What is The Difference Between a Project Quality Management Plan and a QA Project Plan?
A QA Project Plan (QAPP) describes the necessary QA procedures,
quality control (QC)
activities, and other technical activities that will be implemented for a
specific project or program.
A Project Quality Management Plan describes an organization’s quality system,
i.e., its systematic approach to quality
assurance. The Quality Management Plan is also know as the Quality Management System, (QMS). ISO 9001 provides guidelines for one type of QMS.
What is a QA Project
Plan?
A QAPP describes the activities of the data operations project involved with the acquisition of QA information whether generated from
direct measurements activities, collected from other sources, or compiled from
computerized databases
and information systems.
What is The Purpose of The QAPP?
The QAPP documents the results of
a project’s technical planning process, providing in one place a clear,
concise, and complete plan for the
QA data operation and its quality objectives and identifying key project
personnel.
May I Combine a
Project Quality Management Plan and a QA Project Plan into one Document?
Yes.
With permission of the QA Manager of the organization sponsoring the work, these two
documents may be combined into a single document for small programs, grants,
and contracts. The
combined document should address satisfactorily all the elements of both
documents.
What Are The Benefits
of a QA Project Plan?
The QAPP communicate,
to all parties, the specifications for implementation of the project design and
to ensure that
the quality objectives are achieved for the project.
It does not guarantee
success every time, but the
prospects are much higher with a QA Project Plan than without one. Up-front
planning eliminates approaches that do not work well (or not at all), which potentially reduces the cost of lost time and rework.
Implementation as prescribed, with
appropriate QC
practices employed, increases efficiency and provides for early detection of
problems, either in the field
or in the laboratory. This again saves time and money from the rework and
enables the ability to make
decisions more expeditiously. For example, following calibration procedures help assures the
credibility and usability of data generated by laboratory instruments.
When Should a QAPP Plan Be Prepared?
Prepare a QAPP is prepared either part
of or after the project planning process. But in all cases, the QAPP
should be completed and
approved before the starting the project.
PDCA Complete is an organizational task management system with built-in continuous improvement tools. Includes projects, meetings, audits and more.
Built by Quality Assurance Solutions.
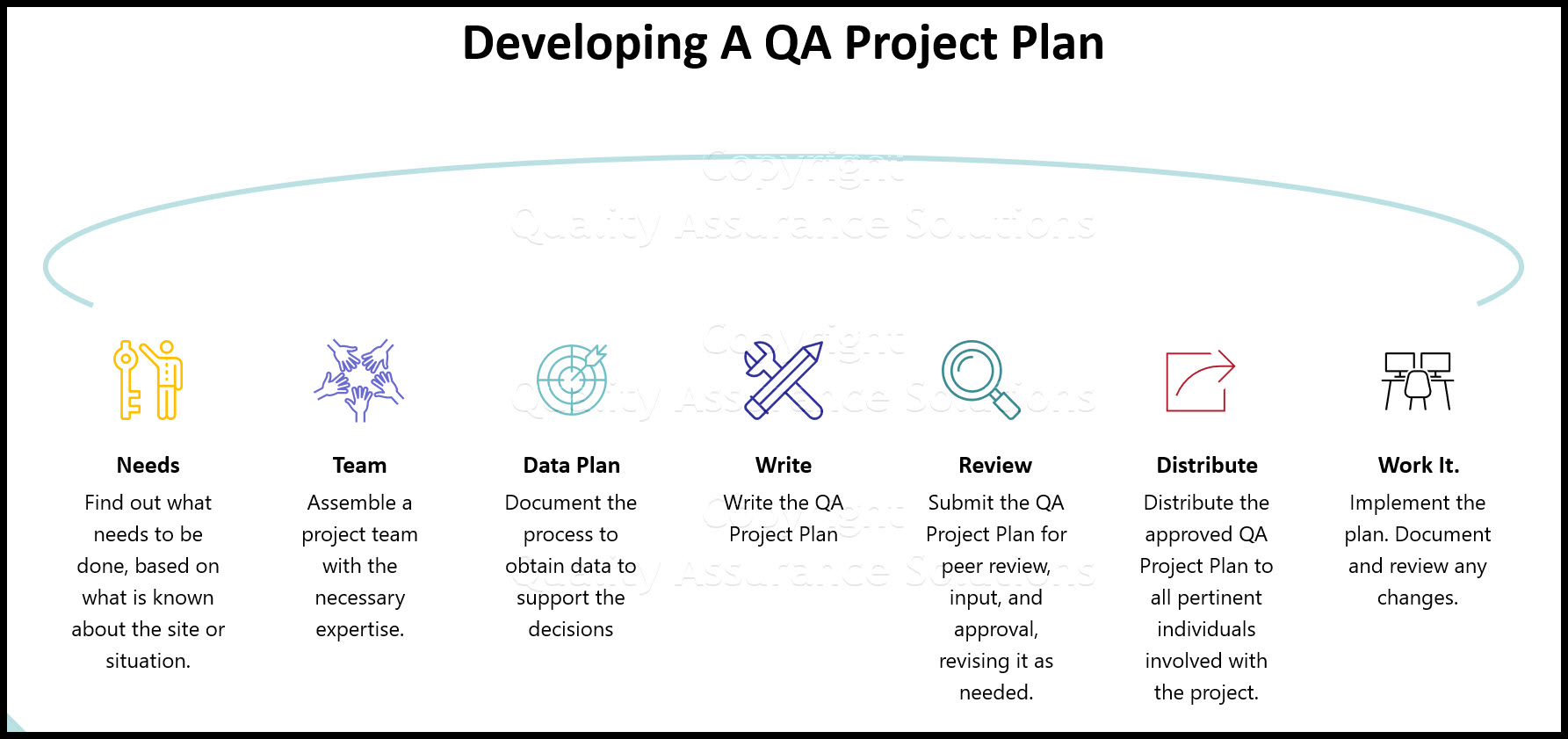
How Do I develop a QA
Project Plan?
The
following is a brief summary of the process:
- Find out what needs to be done, based on what is known about the site or
situation. - Assemble a project team with the necessary expertise.
- Plan what can be done, or what will be done to obtain data of known quality
that are good
enough to support the decisions to be made or the study questions to be answered. - Write the QA Project Plan.
- Submit the QA Project Plan for peer review, input, and approval, revising it
as needed. - Distribute the approved QA Project Plan to all pertinent individuals involved
with the project. - Begin work while implementing the plan, but remember to: document any changes
in the QA Project Plan, get re-approval before initiating the change, and then distribute
the updated version.
Should a QAPP be approved before work begins?
Yes.
Complete all work involving the collection
or use of data with an approved QAPP. A QA Project Plan should
generally be approved before any data collection operation starts.
Advance
approval ensures that the team completed all the planning steps, including connecting actions with needs. Clear documentation increases the likelihood that the project achieves its intended
results. If the plan is not approved before work begins, a stop-work order may
be issued.
When Should I Revise
my QAPP?
When
changes affect the scope, implementation,
or assessment of the outcome, revise the plan to keep project information
current. The
Project Manager, with the assistance of the QA Manager, determines the impact
of any changes on
the technical and quality objectives of the project.
For
long-term projects, such as multi-year monitoring programs, review the QA Project Plan annually by the Project Manager to determine the need for revision.
PDCA Complete is an organizational task management system with built-in continuous improvement tools. Includes projects, meetings, audits and more.
Built by Quality Assurance Solutions.
When Should I Submit a Revised QAPP For Review?
When
a substantive change warrants, the originator of the QAPP revises the plan to document
the change, and then submits
the revised plan to the approving authority. Implement the change only after
approval of the revision. Send the revised plan to all the individuals cited in the
distribution list.
How Long Do We Keep the QAPP After The Project Ends?
Document
retention should comply
with the approving organization’s specifications first, and the specifications
of the organization performing
the work second.
What is Generally Contained in a QAPP?
Divide the QAPP into four basic element groups:
- Project Management Data Generation
and Acquisition; - Assessment
- Oversight
- Data Validation Usability
A QAPP that addresses the basic elements defines and describes the
following:
- Who uses the data;
- What are the project’s
goals/objectives/questions or issue - What decision(s) will be made from
the information obtained; - How, when, and where project
information will be acquired or generated; - What possible problems may arise and
what actions can be taken to mitigate their impact on the project; - Specify the type, quantity, and quality of
data; - How “good” those data have
to be to support the decision to be made; - How the data will be analyzed,
assessed, and reported.
What
if some of the elements do not apply? Plans vary in their level
of complexity,
based both on the nature of the work being performed (such as the collection of
new data or
the use of previously collected information), available resources, and the
intended use of the data.
PDCA Complete is an organizational task management system with built-in continuous improvement tools. Includes projects, meetings, audits and more.
Built by Quality Assurance Solutions.
Can Additional Information be Specified Beyond The Standard Elements?
The
organization sponsoring or overseeing the work may specify additional
information to clarify project-specific
information.
If This Information is Documented in Other Places, Do I Rewrite That Information Into This QA Project
Plan?
Referring
to existing documents can reduce the plan preparation and review
time and length. Any documents prepared before the QAPP, such as
standard operating
procedures (SOPs), sampling and analysis plans (SAPs), work plans, assessments,
literature files, and data sets from other projects, may be appended.
Alternatively, they may
be incorporated by reference, if those sources are readily available to both
reviewers and project personnel
who implement the QAPP.
How Long is a QAPP?
A
Plan should have enough information to describe
project objectives and details. The number of pages needed to address this
information varies
with the complexity of the project and intended use of the information.
A plan
for some QA
data operations may involve a qualitative discussion of the experimental
process and its objectives,
while a plan that describes a complex project may involve extensive documentation
to adequately describe activities.
May I Use The Same Plan For Standard Activities?
Multi-year
projects, and projects
conducted at multiple sites, containing the same project objectives and sampling
and analytical processes,
may be described in a generic QAPP. You may describe site specific
activities in supplements,
for example, separate field sampling plans. Review generic plans annually to
determine if any
changes are necessary.
What is The Role of Systematic Planning in Developing The QAPP?
Systematic planning
is a process in which you identify the problem to be investigated or the
decision to be made, and
then define the project’s objectives, the type, quantity and quality of
information needed, the technical
and quality control activities, and the level of oversight to ensure
satisfaction of project criteria.
PDCA Complete is an organizational task management system with built-in continuous improvement tools. Includes projects, meetings, audits and more.
Built by Quality Assurance Solutions.
Who is Included in Developing The QAPP?
Project
planning necessitates the coordinated
efforts of many individuals, such as those who generates information and
those who uses
the information or make decisions based on that information. These individuals
include:
decision makers,
project managers,
regulators,
stakeholders,
modelers,
risk assessors,
and
technical staff (for example,
hydrologists, chemists, data validators, samplers, and statisticians).
In
addition, include peer reviewers
and individuals with varied expertise to ensure it sufficiently addresses technical areas, thus
helping to minimize problems during implementation.
Who Ensures That The Plan is Written?
Those
who are both involved in planning
the project and experienced in the operations, prepare and/or assist in the preparation
of the QA Project Plan. For
internal projects, the Project Manager or Principal Investigator is generally responsible
for overseeing plan preparation. For externally funded projects, the recipient
of the funds is usually
responsible for project plan development.
Who Reviews The Plan?
This
varies with each organization. Reviewers with expertise in the project
specific areas, such as
- program managers (decision makers),
- QA staff
independent of project management,
and - project field and laboratory technical staff, should review the plan.
What is Included in a
QAPP Review?
Reviewers
should:
- Ensure that the information is
accurate and complete; - Ensure that all appropriate elements
are addressed; - Ensure that the plan identifies the
project’s technical and quality objectives, and that the intended measurement
and data acquisition methods will satisfy these objectives; - Confirm that the planned assessment
procedures will be adequate to evaluate the project - Confirm that there is a process to
identify any limitations on the use of the data.
These
reviewers may also use tools, such as a checklist, in their review.
PDCA Complete is an organizational task management system with built-in continuous improvement tools. Includes projects, meetings, audits and more.
Built by Quality Assurance Solutions.
Who Approves The QAPP?
The
approving authority will vary with the individual organization.
The organization’s Project Quality Management Plan establishes how, when, and
by whom development,
review, approval, and effective oversight of QA Project Plans should occur.
This includes
processes for extramural organizations that prepare QA Project Plans.
The
Project Manager or Project Officer, and the QA Manager usually approves the QA Project
Plan. For extramural projects, the responsible organization’s Project Manager,
or Principal Investigator,
and QA Manager may review and approve the QA Project Plan, and then submit it
for customer
approval. It is also beneficial if other key staff, such as the laboratory directors and prime contractors and
subcontractors, sign the plan to indicate their review and approval
What Types of Approvals Exist?
In
situations where only non-critical deficiencies in a QAPP have not been resolved (such as a final organizational chart or a data
analysis procedure that
will not be followed for weeks), conditional approval may be given to allow the
project to start while
these deficiencies are being resolved. The plan is then resubmitted for approval
when the information
is finalized. The concept of conditional approval, however, varies with
individual organizations;
some organizations may not permit conditional approval of a QA Project Plan.
Who Gets a Copy of The
QAPP?
All
personnel involved in the project should retain
or have access to the current version of the QAPP. This may include
the Project Manager,
laboratory manager, field team leader, modeler, QA Manager, data reviewers, and
any essential
contractor and subcontractor personnel involved with the project.
Who is Responsible For Implementing QAPP?
The
organization performing the
work is responsible for ensuring that the QAPP is implemented as
written and approved, whether
this work is conducted by contract personnel or in-house personnel. Ultimately
the Project Manager
is responsible for project activities. A clearly written QA Project Plan will
help the Project Manager
implement the plan, because all project personnel will understand the
specifications before the start
of data generation activities.
|
Quality Assurance Solutions Robert Broughton (805) 419-3344 USA |
 |
منبع: https://www.quality-assurance-solutions.com/QA-Project-Plan.html